A 78-year-old male with no relevant medical history was diagnosed with atypical carcinoid in 2012 and underwent left upper lobectomy with curative intent. Three years later, the patient presented with a single local recurrence, and a left pneumonectomy was performed. Twelve years after the initial diagnosis, a CT scan was performed because of dyspnea, revealing multiple round lesions in the tracheobronchial tree (Figures 1A and 1B). Bronchoscopy showed several polypoid lesions (Figures 1C and 1D), and cryobiopsies were performed. Pathological examination showed well-differentiated neuroendocrine cells, and immunohistochemistry showed a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50%, as well as positivity for CD56, synaptophysin, and chromogranin A, the final diagnosis being atypical carcinoid (Figures 1E and 1F). During a second bronchoscopy, laser and electrocautery resection of the tracheobronchial lesions was performed.
The most common site of carcinoid tumors is the gastrointestinal tract, followed by the tracheobronchial tree.(1) Diagnosis requires a biopsy with histological confirmation, and atypical carcinoids are less common than typical carcinoids, the recurrence rate for the former being higher than that for the latter.(1,2) Atypical carcinoid usually presents as a peripheral lung lesion or a solitary endobronchial lesion.(1) We found only two case reports of multiple tracheobronchial lesions, with tracheobronchial spread occurring seven and eight years after surgical treatment, respectively.(1,2) In the case reported here, tracheobronchial spread occurred nine years after the second surgical procedure and 12 years after the first.
INFORMED CONSENT Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of his clinical data and the use of diagnostic images.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS AJS, JI-V, and JF: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, validation, research, and writing—review and editing. AJS and JI-V: data curation, software, and writing—original draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST None declared.
REFERENCES 1. Surani S, Tan J, Ahumada A, Surani SS, Sudhakaran S, Varon J. Delayed Recurrence of Atypical Pulmonary Carcinoid Cluster: A Rare Occurrence. Case Rep Pulmonol. 2014;2014:620814. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/620814
2. Amemiya R, Takada I, Yazaki Y, Ono S, Kou K, Morishita Y, et al. Atypical carcinoid with multiple central airway metastases: A case report. Respir Med Case Rep. 2021;34:101550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmcr.2021.101550

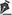
 English PDF
English PDF
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to cite this article
How to cite this article
 Submit a comment
Submit a comment
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Pocket
Pocket